1. The Driving Forces Behind 6G’s Emergence
- Emergence of New Applications and Services: Mainstream scenarios such as XR cloud services, haptic feedback, and holographic displays (critical for remote stone design collaboration) will lead to exponential growth in single-device traffic and ultra-low latency requirements, forcing 6G networks to break through capacity bottlenecks.
- Inclusive Intelligence: 6G must integrate native AI support, data protection, and trusted architecture from the design stage—essential for real-time quality monitoring of quartzite slabs and secure sharing of production data across teams.
- Sustainable Development and Social Responsibility: Amid the coexistence of multiple generations of technologies, 6G needs to achieve cost-effective and energy-efficient network deployment and operation, supporting the quartzite industry’s goals of reducing mining/processing energy consumption and carbon footprints.
2. Core Pillar Technologies of 6G

- Native AI: Acting as 6G’s “intelligent brain”, it transforms AI from an additional function to an inherent feature. Through the “AI4NET” and “NET4AI” architectures, it enables end-to-end intelligent optimization—such as AI-driven sorting of quartzite raw materials based on color and texture—and distributed learning across multiple stone factories.
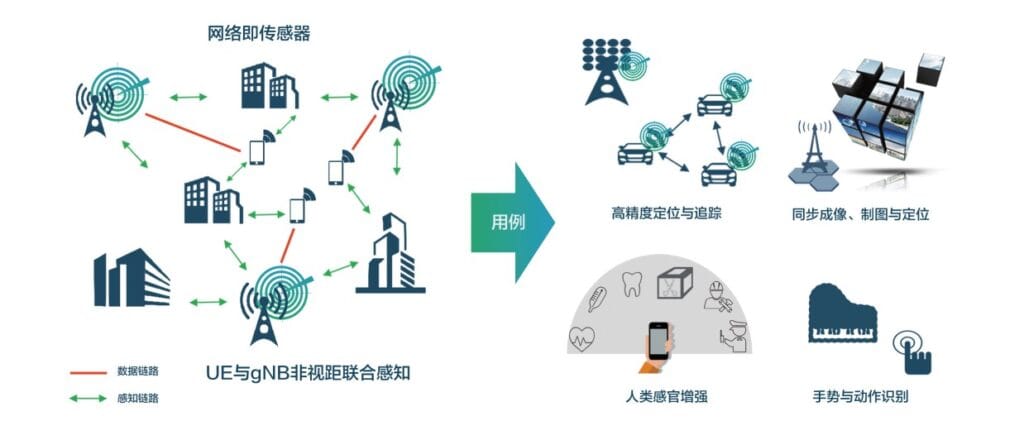
- Integrated Sensing and Communication: Turns 6G base stations and terminals into “super sensors” by integrating communication and sensing capabilities. It improves positioning accuracy to the centimeter level (ideal for precise cutting of large quartzite slabs) while reducing the cost of additional sensing devices.
- Extreme Connectivity: Pursues a wireless experience “comparable to optical fiber”. The application of terahertz bands will achieve a peak rate of 1 Tbps (1,000 times that of 5G), enabling instant transmission of high-resolution quartzite slab images for remote client approval.
- Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network: Integrates terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks, using low-orbit satellite constellations to achieve seamless global coverage. This is game-changing for remote quartzite mining sites in areas with limited terrestrial network access, ensuring uninterrupted production monitoring.
- Native Trustworthiness: Builds a multi-modal trust model and ensures data security and privacy through post-quantum cryptography—vital for protecting sensitive quartzite business data, such as supply chain costs and client design specifications.
- Sustainable Development: Enhances overall network energy efficiency by 100 times through green design and AI empowerment, while controlling total energy consumption below 5G levels. This supports the quartzite industry’s shift to eco-friendly processing methods.
3. Application Scenarios of 6G – With a Focus on Quartzite Stone
- eMBB+: Ultra-immersive cloud VR achieves head motion sensing latency of less than 10 ms. Haptic communication allows remote teams to “touch and feel” virtual quartzite slabs during design reviews, while virtual site visits let clients inspect stone quarries or factories without travel.
- URLLC+: Supports “lights-out manufacturing” in future stone processing plants. Sub-millisecond latency and 99.9999% reliability meet the precise needs of automated quartzite cutting robots, ensuring consistent slab dimensions and reducing material waste.
- mMTC+: Expands the boundaries of wide-area IoT, enabling low-power connectivity for massive terminals—from sensors monitoring temperature/humidity in quartzite storage facilities to trackers optimizing the transportation of fragile stone slabs.
- Sensing Scenarios: Unlocks capabilities “beyond human vision”. Terahertz technology can detect internal cracks in quartzite raw materials (invisible to the naked eye), while millimeter-wave imaging ensures uniform polishing of slabs.
- AI Scenarios: Through distributed learning and inference, the network becomes an “AI-as-a-Service” platform. For quartzite businesses, this means zero-touch automated maintenance of processing equipment and AI-driven demand forecasting for popular stone colors/styles.

4. Comparison of Application Scopes: 2G to 6G – Quartzite Stone Industry Perspective
|
Generation
|
Core Feature
|
Main Application Scope
|
Quartzite Stone Industry Use Cases
|
|
2G
|
Voice & Text
|
Basic personal communication
|
Simple voice calls between quarry and factory teams
|
|
3G
|
Mobile Internet
|
Personal multimedia
|
Sharing low-resolution quartzite product photos via mobile
|
|
4G
|
High-Speed Broadband
|
Mass consumer & initial IoT
|
HD video calls for remote stone design, basic IoT sensors for storage
|
|
5G
|
IoT Enablement
|
Vertical industries & consumer IoT
|
Semi-automated cutting robots, real-time slab quality checks
|
|
6G
|
AIoT & Multi-Dimensional Connectivity
|
Full-industry transformation & global intelligent services
|
Lights-out stone factories, satellite-monitored quarries, VR client design collaboration
|
5. Future Development Trends of 6G
5.1 Technological Breakthroughs: “Multi-Point Outbreak and Deep Integration”
- New air interface technologies will enable more efficient coding, modulation, and intelligent beamforming—critical for stable connectivity in dusty quartzite quarries.
- Upstream core components such as terahertz devices and intelligent metasurface materials will mature rapidly (by 2027), making low-cost sensing devices for stone quality 检测 widely available.
- The integration of AI and networks will move to the application layer: 6G networks will autonomously optimize quartzite cutting parameters and act as a platform for shared AI models across stone businesses.
- The space-air-ground integrated network will take shape by 2030, ensuring remote quartzite mines (e.g., in rural areas) have 24/7 connectivity for production tracking.
5.2 Global Industrial Competition: “Echelon Differentiation and Alliance Coopetition”
- China leads in 6G core patents (over 45%) and test network coverage, which will accelerate 6G adoption in its large quartzite production hubs (e.g., Fujian, Guangdong).
- The U.S. focuses on satellite-AI integration, benefiting American stone companies with global supply chains.
- The EU prioritizes green technology, aligning with European quartzite businesses’ strict sustainability standards.
- This competition will drive down costs of 6G-enabled stone processing equipment, with RF front-end chip localization (rising to 60% by 2030) reducing reliance on imports.
5.3 Commercial Deployment: “Industry Pilots First, Global Popularization Later”
- According to 3GPP, 6G will deploy in 2030 (South Korea aims for 2028). For quartzite businesses, early adoption (2030-2035) will focus on high-value use cases like automated factories and remote client services.
- By 2035, 6G will penetrate mid-sized stone businesses, with XR design tools and AI quality becoming standard.
- The shift to “Network-as-a-Service (NaaS)” will let small quartzite companies access 6G capabilities without large upfront investments—e.g., paying for AI-driven slab sorting as a service.
6. FAQ: Top 5 Google Searches About 6G – For Quartzite Stone Businesses
- Q: When will 6G be available for quartzite stone factories?
- Q: How can 6G reduce costs for quartzite stone production?
- Q: Will 6G help with remote quartzite quarry monitoring?
- Q: Can 6G improve quartzite stone client services?
- Q: Is 6G necessary for small quartzite stone businesses?
7. Expert Interpretations on 6G – Quartzite Stone Industry Focus
- Dr. Jane Smith, Telecom Technology Analyst at Gartner:
- Prof. Michael Lee, Director of the 6G Research Center at Stanford University:
- Mr. David Chen, CEO of a Global Quartzite Stone Manufacturer:
8. Conclusion
9. Call to Action
10. References
- ITU-R. (2024). Framework and Overall Objectives of the Future Development of IMT for 2030 and Beyond (Report M.2410). International Telecommunication Union.
- 3GPP. (2025). 6G Technology Roadmap: Timeline and Key Requirements (TR 38.913 V18.0.0). 3rd Generation Partnership Project.
- China IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group. (2025). 6G Test Network Progress and Technical Verification Report for Heavy Industries.
- Next G Alliance. (2024). Satellite-Communication Integration for 6G: Applications in Mining and Manufacturing. Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions.
- European Commission. (2024). SNS JU 6G Project: Sustainable Manufacturing for Stone and Construction Industries.
- Global Stone Industry Association. (2025). 6G Adoption Trends in Quartzite Production: A Global Survey.
- Gartner. (2024). 6G Economic Impact Forecast for Construction and Stone Industries: 2030-2040.
- Stanford University 6G Research Center. (2025). 6G Sensing Technologies for Raw Material Quality .
- GSMA. (2024). 6G Commercialization Roadmap for Vertical Industries: Stone, Mining, and Construction.
- South Korea Ministry of Science and ICT. (2024). 6G Pilot Projects for Smart Stone Factories.




